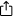The Risk of Inadequate Data Erasure: Real-Life Consequences and Case Studies
| Summary: Inadequate data erasure poses significant risks. It can lead to privacy breaches, financial penalties, and reputational damage. In this blog, we use real-life cases to highlight the consequences of a security breach. Further, we emphasize the need for robust solutions like Bitraser for secure data disposal and compliance. |
|---|
Cybercrime is on a terrifying rampage. It is poised to cost companies an astounding $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. That is up from a mere $3 trillion in 2015.
What’s worse is that it takes companies an average of 197 days to identify such instances. And another 67 days to contain the damages.
Moreover,
- A staggering 45% of companies in the United States have fallen victim to data breaches.
- Companies that encounter a breach witness a significant drop in performance. They are seen lagging behind the market by over 15% after a span of three years.
- Small businesses were the target of 28% of data breaches.
The silver lining is that companies are taking data privacy and cybercrime seriously. Findings from Gartner reveal a global surge in data security expenditure. It soared by 17.5% from 2020 to 2021.
But imagine if you also face data breach risks from the devices that have been discarded.
Yes, that’s possible.
As per The HIPAA Journal, 16 instances of improper device disposal were reported in 2020. These occurrences potentially exposed nearly 600,000 records.
When you sell your old devices or drop them off at dumpsters, what happens to the valuable data they once housed?
We deleted the data before disposing of the device!
Well, that’s not enough.
Even after you press delete, the information that can be retrieved. By anyone with just the right software and a little bit of expertise.
What you need is thorough data erasure.
Not convinced?
Let’s take 3 real-life examples and see how inadequate data erasure led to grave consequences.
Disaster From The Dumpster: Real-Life Consequences Of Inadequate Data Erasure
Data Breach Example 1: The HealthReach Data Breach
Who was involved: HealthReach Community Health Centers
The data:
The breach involved the sensitive and personal information of 101,395 Maine residents. This included:
- Patient names,
- Social Security numbers (SSNs),
- Dates of birth,
- Financial account numbers,
- Lab/test results,
- Insurance details,
- Passwords,
- Security codes, and
- PINs.
To compound the situation, 15,503 individuals from other states were also affected.
What happened:
HealthReach Community Health Center is a healthcare organization based in Waterville, Maine. On September 9, 2021, they found themselves at the center of a massive potential data breach.
The breach originated from a mishandling of data storage devices. Instead of being securely wiped and shredded as per industry standards, several hard drives containing the aforementioned sensitive data were improperly disposed of by an employee at a third-party storage facility. This resulted in a goldmine of personal information falling into the wrong hands.
Upon discovering the breach, HealthReach immediately notified the affected individuals. And they took steps to mitigate the damage. Patients were urged to monitor their accounts and credit reports for suspicious activities. There was no concrete evidence of fraudulent use of the compromised data at that time. But the potential risk was evident.
The consequences:
- HealthReach offered a year of credit monitoring, dark web monitoring, and identity theft protection services to the affected consumers.
- Additionally, a $1 million reimbursement insurance policy was provided through IDX/Transunion. This was to provide some financial protection in the event of identity theft or other issues caused by the data leak.
How could this breach have been avoided?
Properly erasing data from storage devices using a certified data erasure tool like BitRaser Drive Eraser could have easily prevented this breach.
Data Breach Example 2: Morgan Stanley’s Costly Oversight
Who was involved: Morgan Stanley Wealth Management (formerly Morgan Stanley Smith Barney)
The data: Personal identifying information of millions of its customers.
What happened:
Morgan Stanley Wealth Management (MSSB) discovered the consequences of inadequate oversight in data disposal. It occurred between 2015 to 2020.
MSSB had a plan to shut down its data centers in 2016 and enlisted vendors to manage the task. Although a moving firm and IT Corp A jointly applied to take on the project, only the moving firm received official approval.
The agreement between MSSB and this firm specified that IT Corp A would erase or degauss the devices before they were sold again, with MSSB slated to receive between 60% and 70% of the resale profits.
Regrettably, the actual decommissioning deviated from what was agreed upon. The moving firm did collect the hardware and briefly took them to IT Corp A’s location.
While IT Corp A did catalog the devices and even had a trackable database, the promised degaussing was skipped. Several devices were put up in the resale market with vital customer data still on them.
MSSB neglected to oversee this database or maintain any form of direct communication with IT Corp A to confirm the devices were being managed correctly. Moreover, MSSB never claimed the resale profits from the moving firm as was outlined in the contract.
The shortcomings in this scenario were several:
- The agreed-upon degaussing, a vital method for data erasure, was overlooked.
- MSSB failed to keep an eye on the database or establish any direct liaison with IT Corp A to ensure the contract’s terms were met.
- No personnel at MSSB checked whether the devices had been adequately wiped before being put back on the market, resulting in the exposure of confidential client data.
To their credit, Morgan Stanley attempted to recover some of these devices. But most of the devices, with thousands of instances of unencrypted customer data, remained unrecovered.
The consequences:
- The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) required Morgan Stanley Wealth Management to pay $35 million to settle claims related to the improper disposal of customer data.
How could this breach have been avoided?
Hiring a specialized data erasure service with expertise in secure data destruction could have averted this breach.
Data Breach Example 3: Oklahoma State Agencies’ Unsecured Data Resurfaces
Who was involved: Oklahoma Corporation Commission
The data: Names and Social Security numbers of 5000 residents stored on a server.
What happened:
The story unfolded when in 2008 Oklahoma City resident Joe Sills purchased surplus state computer equipment at an auction.
Sills stumbled upon a file containing over 5,000 Social Security numbers. The data had not been properly erased, leaving sensitive information vulnerable.
The server in question had a history of use by the State Tax Commission. And, more recently, was used by the Corporation Commission. The Social Security numbers were likely associated with trucking industry data.
Sills’ discovery ignited outrage. He rightly feared the potential misuse of the exposed sensitive data.
In response to the incident, the Corporation Commission took swift action. To prevent similar occurrences, they decided to remove hard drives from all surplus computer equipment before sending them to state auctions.
The consequences:
- Details about specific penalties or fines aren’t available.
- However, the reputational damage and potential legal consequences could have been significant.
How could this breach have been avoided?
Implementing a standard protocol for data erasure before decommissioning hardware could have prevented this incident. With a reliable data erasure tool like BitRaser, this task could have been easily performed in-house.
Avoiding Dumpster Disasters With Bitraser
The lack of proper data erasure led to significant privacy breaches. And result in financial penalties, legal repercussions, and reputational damage.
However, these disasters could have been averted. How? Through the implementation of robust data erasure practices.
A reliable data erasure solution like Bitraser could have played a pivotal role in preventing such incidents.
Bitraser: Your Solution for Secure Data Erasure
Bitraser is an advanced data erasure software. It is designed to ensure complete and irreversible destruction of data.
By utilizing Bitraser’s powerful features, organizations (and individuals!) can mitigate the risks associated with data breaches resulting from improper data disposal.
How to use BitRaser?
Some features of BitRaser include:
- Bitraser follows industry-standard erasure algorithms. This provides certified data erasure that complies with data protection regulations.
- Even for devices not under the organization’s immediate control, Bitraser allows remote erasure. This avoids security breaches even from devices beyond physical possession.
- Bitraser’s data verification feature confirms the successful erasure of data. This provides an audit trail that proves compliance with data disposal policies.
- Bitraser generates detailed reports of the erasure process. This offers transparency and documentation for compliance audits and legal requirements.
As demonstrated in the case studies, the investment in proper data erasure today can prevent tomorrow’s data breach risk. So don’t wait, invest in the right data erasure software and avoid any data leaks or privacy breaches.