It’s not evident to the naked eye, but our electronics contain trace amounts of toxic materials. And when our electronics end up in landfills, as most of ours do, the toxic materials pollute the environment around them.
The R2v3 standard lays down the guidelines to prevent this.
In this guide, we’ll tell you:
- What is an R2v3 certification?
- What are the 10 core requirements of an R2v3 certification?
- How data security is ensured by the R2 facilities
What is R2v3?
R2v3 is the acronym for R2v3 Responsible Recycling Version.
The R2v3 standard is a voluntary sustainability standard released by Sustainable Electronics Recycling International (SERI).

The guiding principle of R2v3 standards is to maximise the recycling and reuse of electronics. R2 certification is relevant for:
- IT asset managers
- IT asset destruction services,
- Refurbishing and remarketing services,
- e-Recyclers
Responsible recycling (R2) explains the necessary controls for data security, device testing, device repair, and reuse. This has special significance for e-recyclers because of the nature of their work.
Here are the 5 key things to know about the R2v3 standard.
- R2v3 was released in July 2020. This is the second major update to the R2 standards issued in 2013.
- R2v3 draws a roadmap for the sustainable management of used electronic equipment.
- These standards are meant for the electronics recycling industry. ITAD (IT Asset Disposition) vendors who have R2v3 certified infrastructure enjoy greater trust from corporate IT asset managers.
- They define a system to measure the effect on the environment and the employees in the e-recycling industry.
- The major differences between R2 (2013) and R2v3 are the enhanced requirements. These are in tune with the changes in the type of data storage materials and e-waste recycling processes used.
The 10 Core Requirements of R2v3
For an ITAD service provider to get the R2v3 certification, the infrastructure must meet these requirements, expressed as ‘cores’ in R2v3.
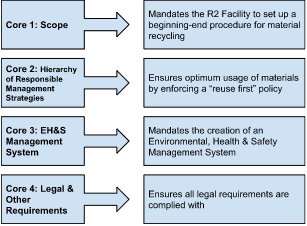
- Scope
An R2 facility must have certified processes and equipment. Activities like collection, renewal, repair, disintegration and recycling are under the scope of R2v3 certification.
This core requirement serves two purposes.
- All R2 processes, from collection to recycling, are identified in the certification.
- It provides the rules for the operations that have been certified.
- Hierarchy of Responsible Management Strategies
Core 2’s purpose is to help extend the life of electronic devices where possible. According to the guidelines, R2v3 compliant facilities must follow a ‘Reuse-first’ policy when dealing with end-of-life electronics.
The hierarchy calls for maximising material recovery. So what can be, must be reused.
This calls for certified data erasure software. If you’re an e-recycler or an ITAD service provider, you need a data erasure software that:
- Is 100% secure
- Complies with all data erasure standards
- Generates a tamper proof erasure certificate
- Works on all device types and with all OS
- Is from a reputed brand with proven expertise in data erasure
Stellar’s BitRaser Data Erasure software ticks all these boxes and many more.
- EH&S Management System
The purpose of Core 3 is to establish a management system that will become the framework for managing the R2 requirements.
You must maintain a certified Environmental, Health & Safety Management System. This is a set of policies and practices an R2-certified facility must follow.
The management system will allow planning, implementing, and monitoring of the safety practices for the workers, the public, and the environment.
The system also addresses some industry-specific hazards in relation to electronics reuse and recycling.
- Legal and Other Requirements
An R2 facility should meet the legal requirements. Core 4 ensures that it does.
The R2v3 standard requires fair and ethical treatment of workers. This Core also addresses that.
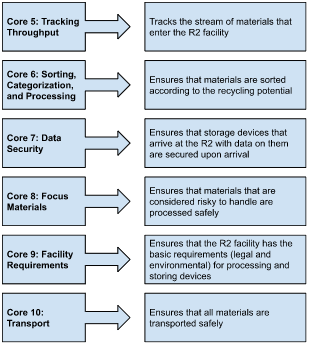
- Tracking Throughput
Core 5 ensures that all materials and equipment are identified, tracked, and managed properly. An R2 facility should maintain the following records.
- Incoming equipment and materials
- Any changes to the inbound stream due to material processing
- Outbound streams of materials
Facilities cannot store materials that incur a cost to process for longer than 1 year.
- Sorting, Categorisation, and Processing
The main intent of Core 6 is to identify the step a component is at in the recycling process. The categorisation helps to verify that the correct steps are followed. The sorting is done according to the guidelines in the REC (R2 equipment categorisation) document.
The REC document defines the processing status, physical condition, and the next level in the R2 processing.
The key steps in the REC document are:
- Identify and segregate storage devices
- Evaluate the devices for reuse potential
- Direct the device to the next REC step based on the REC categories
The processing pathway for equipment should be determined following the hierarchy stated in Core 2.
- Data Security
Data security is a key factor of R2 compliance. All storage devices should be secured immediately after entering the R2 facility. After this, the data is sanitised using one of the following two methods.
- Physical destruction
- Logical and physical destruction methods
Data sanitisation can be outsourced to a verified third party. The recycling facilities don’t have to do the sanitisation themselves.
- Focus Materials
Focus Materials (FM) are equipment that require special handling due to certain risks. The risks could be pertaining to the materials themselves or the process used to recover the separate metals and reusable elements in the materials.
This requirement ensures that all focus materials are identified and handled safely. The facility must
- Come up with a Focus Material Management Plan. The plan should outline the methods used for handling FM.
- Verify downstream vendors
- Facility Requirements
All R2 facilities must have a legally compliant environment for processing and storing materials. There are the 3 key facility requirements. They address
- The conditions for where and how items can be stored and processed.
- The site risks. The facility should also have adequate insurance to cover those risks.
- Facility closure plans. This is to ensure there is no toxic leakage when the plant isn’t operating.
- Transport
The facility should ensure the safe, secure, and legal transportation of all materials.
If the materials are identified as harmful (FM) they will require special packaging and handling. Data storage devices should be secured before transport. The transport of all materials must comply with the requirements stated in the Legal Compliance Plan.
Overview of the 10 Core Requirements
The Data Security Requirements for Meeting R2v3 Compliance
In the R2v3 standard, Core 7 talks about data security. There are 4 areas for meeting the R2v3 requirements under core 7. They are:
- Documentation
The R2 facility must maintain documentation on the data sanitisation plan they intend to follow. The document should contain the following information.
- The type of device and the R2 facility that will sanitise it.
- The security measures in place at the R2 facility that ensure the safety of the data held there.
- The methods used for data sanitisation are based on device type.
- Information about the third-party vendor hired (if any) that will perform data sanitisation.
- Methods to show the efficiency and verification of the data sanitisation method.
- Security
The physical access of data storage devices at R2 facilities should be limited. These are the guidelines to follow to effectively secure the devices.
- The facility should have a security program that limits the access of the storage devices. This should be based on the electronic equipment, data sensitivity, and the needs of the suppliers.
- The facility must have authorisation levels for accessing the devices.
- An incident response procedure should be implemented in case of a data breach.
- Process
This defines the process used for receiving and sanitising data storage devices.
- If the R2 facility receives data storing equipment, an acknowledgement receipt should be sent to the supplier.
- Details of data sanitisation should be provided.
- The data should be sanitised timely and effectively.
- Notification
For proper R2v3 Compliance, the facility should have a process of notifying suppliers, any third parties, or legal authorities if there is
- A change in the vendors responsible for device processing
- A data breach incident
The Benefits of an R2v3 Certification
The impact of data sanitisation and e-waste recycling is felt most by the workers of the industry and those living close to the R2 facility. The R2v3 standard does its duty to best negate the impact these activities have.
The 10 core requirements ensure that safe and sustainable practices are followed at all R2 facilities. In doing so, it reduces the impact of e-waste recycling on both the environment and the employees.




