Whacking your device with a hammer surely is an effective way to destroy data. But you wouldn’t want to resort to that for an expensive laptop, would you?
Various devices store data in different ways. So some methods work well with one device that wouldn’t change a thing for another device.
In this guide, we discuss the most effective data destruction strategy according to device types. Read to learn about:
- The factors that influence the destruction method
- How to make your decision
- Data erasure methods according to device types
- The NIST 800-88 standard
- How to apply the standard to 5 common device types
Factors That Influence The Choice of Destruction Method
The ultimate purpose of a data erasure strategy is to ensure the complete removal of data such that it’s not recoverable. There are several data erasure methods. Each adheres to a certain standard and is more suitable for specific devices.
Here are the factors to consider when choosing a data destruction strategy:
- Privacy concerns and risk tolerance
Data erasure methods like disk formatting and deleting can help you save money. But they are fairly easy to override and recover data. So you would select these methods for less sensitive data.
-
Type of storage device
Degaussing doesn’t work on SSDs but is effective for hard drives. Similarly, some erasure methods are effective for some devices.
-
Environmental concerns
Physical destruction renders the device unusable making it another addition to landfills.
According to a report by the Central Pollution Control Board, India generated 1,014,961 tonnes of e-waste between 2019-2020. E-waste can leak toxic matter into the ground and water sources. The most dangerous effects of this is kidney and neurological disorders.
Proper management of e-waste is crucial if we’re to reduce our impact on the Earth. That’s why organisations have sustainability policies in place. And if they do, software-based erasure methods work the best.
How to Choose the Data Erasure Strategy?
Choosing the best data destruction strategy is up to you and your company’s policies. The best practice when picking a data erasure strategy is to have a standard list of questions. The answers to these questions should reveal the data destruction strategy you should pick.
Here is a decision flowchart that will make the task easier for you:
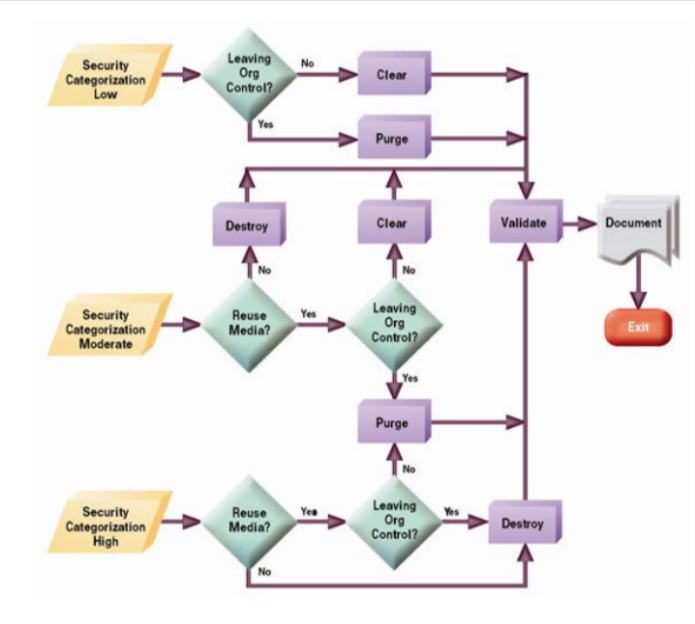
Overview of Media Types and The Ideal Data Erasure Strategy
As mentioned previously, the data erasure strategy depends on the storage device. The following table relates the data erasure strategy to the device types.
| Device Type | Storage Mechanism | Best Data Removal Method |
|---|---|---|
| HDD | Non-volatile magnetic | Physical and digital: Multi-pass pattern wiping, disintegration, incineration |
| SSD | Non-volatile solid-state memory | Physical and digital: Multi-pass pattern wiping, disintegration |
| Flash Drives and USB | Non-volatile solid-state memory | Physical and digital: Multi-pass pattern wiping, disintegration, degaussing |
| Magnetic Tape | Non-volatile magnetic | Physical methods: degaussing, incineration, disintegration |
| CD-RW/DVD-RW | Write many digital optical disk | Physical methods: abrasion, incineration, disintegration |
NIST SP 800-88 Standard of Data Eraure Strategy for Storage Device
The NIST SP 800-88 is a guideline that outlines how to safely erase data. Three data erasure methods are used to sanitise media under NIST 800-88. These methods are device and data-specific.
These are the sanitization techniques defined by the guideline:
- Clear
Logical techniques to sanitise data are applied through standard Read-and-Write commands such as rewriting. Block erase, and cryptographic erase are some other data erasure methods used under the Clear technique.
Effective for: ATA Hard Drive, SSDs
- Purge
This is typically used for confidential data as it makes data recovery impossible. Degaussing and cryptographic erasure are two of the data erasure strategies used.
Effective for: HDDs and SSDs
- Destroy
Destroying is a purely physical data destruction strategy. You can use techniques like incineration and shredding to sanitise data.
Effective for: Almost all types of devices
The NIST 800-88 Standard for Data Destruction: 5 Most Common Device Types
Here are the recommended methods to sanitise 5 different devices using the NIST 800-88 standard.
- HDDs
Hard disk drives are non-volatile storage devices that maintain data even when turned off. HDDs are installed in laptops, CPUs, and servers, among many others.
Here’s how to apply the NIST 800-88 standard to HDDs.
| Clear |
|
| Purge |
|
| Destroy |
|
If you’re using the clear or purge data erasure strategy, you should verify the destruction, unless you’re unable to do so.
- External HDDs
Internal and external don’t have many differences in the way they store data. Their location is the biggest difference. And it is something that makes external HDDs more vulnerable to outside threats like theft.
| Clear |
|
| Purge |
|
| Destroy |
|
If you’re using Clear or Purge methods, you must verify that the data erasure strategy was successful.
Some external HDDs can have encryption features that have hidden storage areas. So always check with the manufacturer whether your device has such an area and how to erase files from that location.
- SSDs
Solid-state drives use integrated circuit assemblies to store data. SSDs are typically harder to sanitise than HDDs.
Here are some ways to sanitise SSDs following the NIST 800-88 standard:
| Clear |
|
| Purge |
|
| Destroy |
|
- Mobile phones
This is probably the most commonly used storage device across the world. It is also the most discarded. So you will need a very secure method to sanitise the data if you’re going to throw away old phones.
Here are some ways to do that for iOS devices:
| Clear |
|
| Purge |
|
| Destroy |
|
- USB Removable Media
Pen Drives, Thumb Drives, Memory Sticks, and Flash Memory Drives are all examples of USB removable media.
| Clear |
|
| Purge |
|
| Destroy |
|
USB devices are comparatively inexpensive. So destroying it would be the most effective way to sanitise the media.
Data Destruction Strategy Decisions
NIST 800-88 is the golden standard to abide by when sanitising your devices. If you need the device intact, then using NIST-certified software is a safe bet to sanitise your device. You can use BitRaser, a data eraser software that follows the golden standard.
If the device is disposable, then you can use physical destruction techniques. That will leave absolutely no trace of your data.




