Overview of BitLocker Encryption
Microsoft Windows is, without a doubt, the most popular operating system used in desktops and laptops with over 80% of the market share. With such popularity comes unwanted attention from hackers. Starting in 2004 Microsoft launched a safety initiative that allowed users to encrypt their hard disks.
The feature known as BitLocker debuted with Windows Vista in 2006. Bitlocker is a standard safety feature on Windows 11. The purpose of BitLocker drive encryption is to thwart others from stealing information stored on your drive. You can use device encryption or BitLocker not only on desktops and laptops but also on all versions of Windows from Server 2008 onwards.
Windows versions that offer BitLocker:
- Windows Vista Ultimate and Enterprise editions
- Windows 7 Ultimate and Enterprise editions
- Windows 10 Education, Pro, and Enterprise editions
- Windows 11 Education, Pro, and Enterprise editions
- Server—all versions from Windows 2008 onwards
Windows 11 Home does not offer Bitlocker.
Key Features of BitLocker Drive Encryption
Very safe:
BitLocker uses the AES or Advanced Encryption Standard presented by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology. It uses 128-bit encryption. Using the world’s fastest supercomputer, it would take 1 billion years to crack a 128-bit AES code. Needless to say, the universe (or the hard drive) won’t survive that long.
Full-drive encryption:
Full drive encryption means you cannot use it to lock one or two files and folders. Initial versions of BitLocker could only encrypt system drives, but now they can work with any drive or partition.
Resource light:
Using BitLocker does not take time. Encryption means each time the file is read, it has to be decrypted and then displayed or used. Despite being robust, BitLocker does not hog CPU or memory resources. Of course, the time to open and close files is going to take longer.
Needs TPM:
Trusted Platform Module is a piece of hardware. It can be a part of the motherboard or the CPU. TPM offers encryption.
What is TPM?
A slightly elaborate explanation of TPM is necessary. Windows 11 will run only on devices with TPM 2.0 found on processors made from 2018 onwards.
TPM is a microprocessor that handles hardware based encryption. Encryption is taxing on the main CPU. A separate processing unit is better.
Previously TPM was a part of the motherboard.
Beginning 2020, Microsoft released the Pluton security processor that would be a part of all Qualcomm, Intel and AMD processors meant for Windows. It is inside the new CPUs but distinct from it.
TPM 2.0, as it is known, has many functions - from encryption for BitLocker to storing biometric data (for Windows Hello).
BitLocker drive encryption for Windows 10 and 11 (which is used by 90% of Windows users currently) prefers that TPM be a part of the CPU. More or less, all CPUs made after 2017 (Intel 8th Generation Coffee Lake and AMD equivalent Raven Ridge) support this feature. For earlier CPUs and motherboards, there are workarounds depending on the generation and features of the motherboard and CPU.
How to Enable BitLocker?
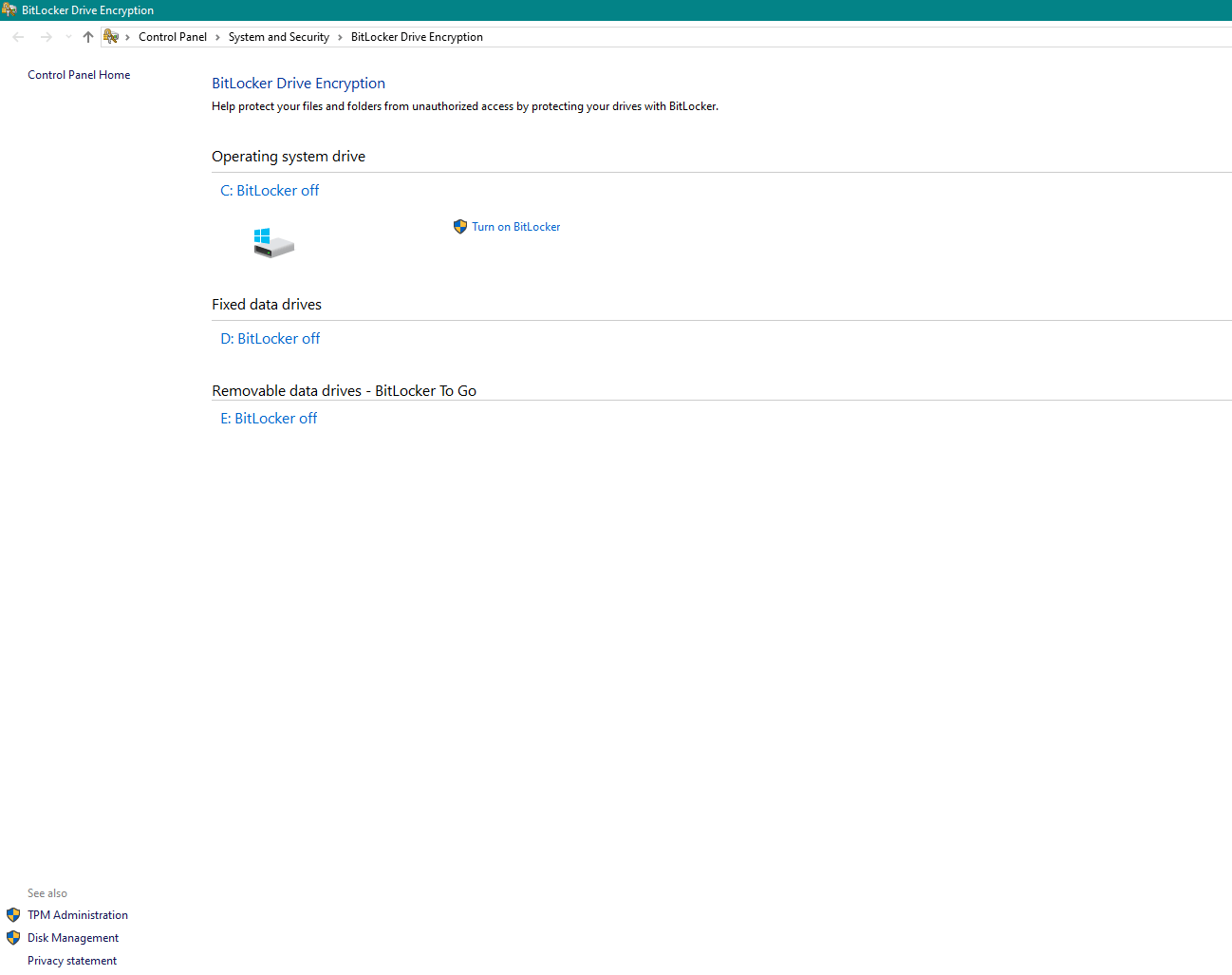
- In the Search bar type Manage BitLocker
- Then select Turn on BitLocker
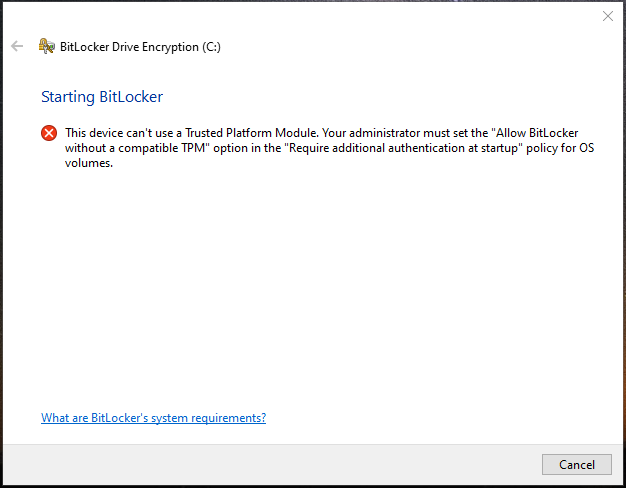
- The PC might show this message.
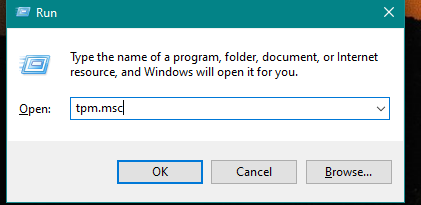
- Check if TPM is enabled by pressing Windows + R key and typing tpm.msc
- Find if TPM is enabled
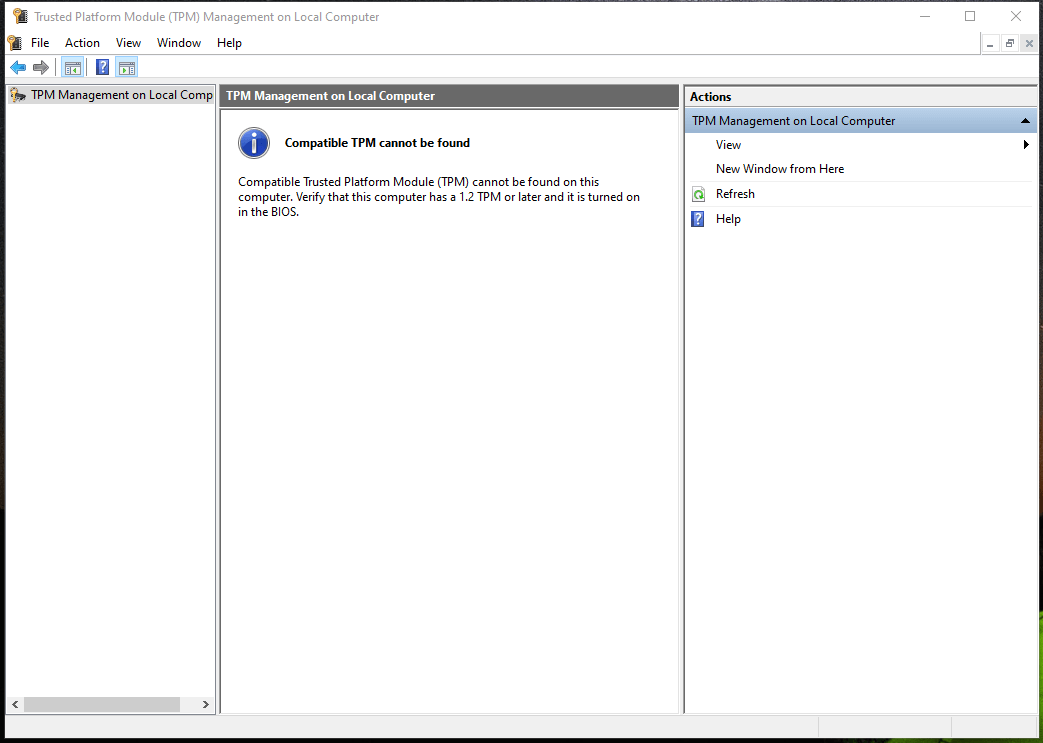
- If TPM is not enabled, go into the settings of BIOS
- To enter BIOS, hit F2, F10, F12, or Del upon restart (depending on the motherboard manufacturer)
- Go to Settings and Enable TPM. The exact steps would depend on the motherboard manufacturer.
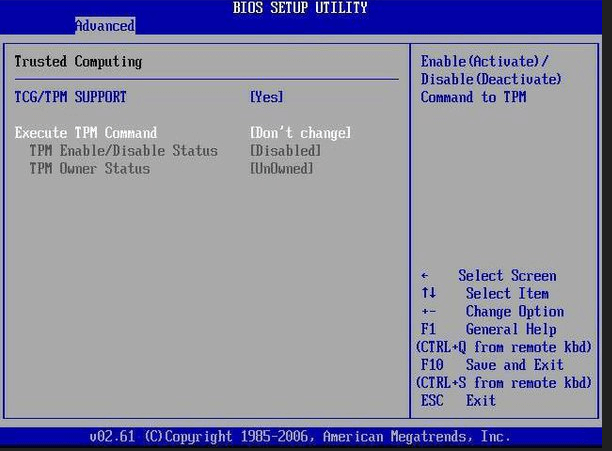
Old fashioned BIOS
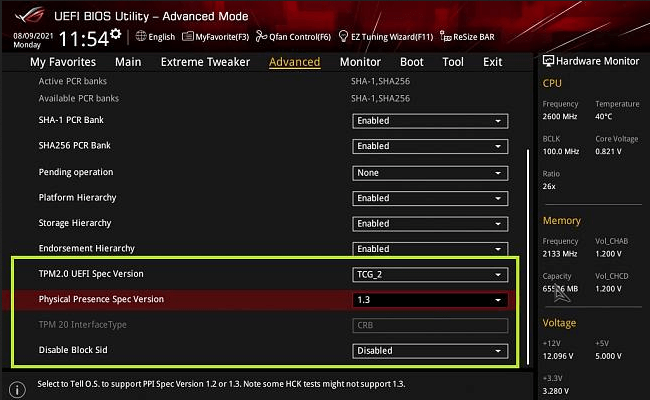
Modern UEFI BIOS (UI varies with manufacturer)
- Once TPM is enabled, go back to Step 1 and click Turn on BitLocker
- A key will be generated and necessary to use the hard drive.
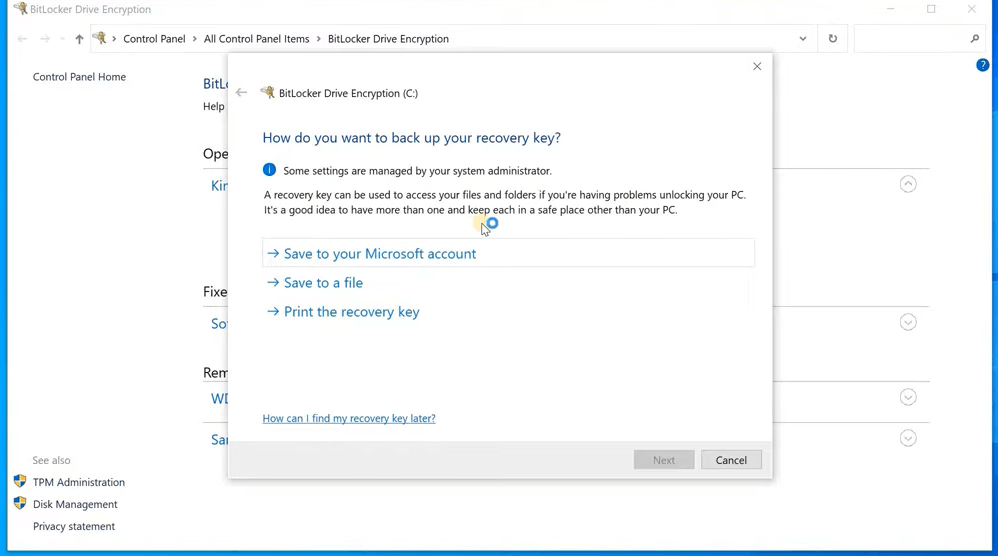
- The key is between 48 characters long and stored in a USB or a file on a different partition. It can also be printed out or stored in a Microsoft account.
- In addition to the key, you can also choose a PIN for extra security.
- Once the key has been set, Windows will ask permission to encrypt the drive. The first time takes a while since there are many files. New files are encrypted as soon as they are created and modified.
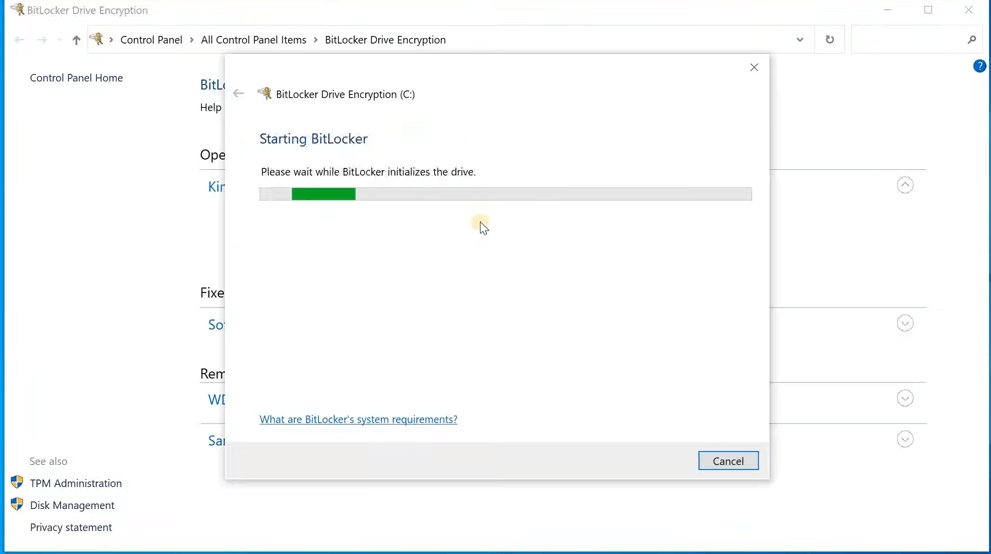
Note- This is a brief overview of BitLocker. BitLocker has many settings and exploring each is beyond the scope of this text.
- To learn more about TPM and BitLocker visit Microsoft tutorials in these links.
How Safe is BitLocker?
BitLocker without TPM (earlier machines running Windows 7) is not very secure. TPM can lock itself if there is a brute force attack at 32 attempts. This makes it very secure.
In case the hard drive has an encryption level (as many SSDs do) then Windows may not encrypt it (because double encryption does not work).
As of this moment, the user has to set an SSD password and enable SSD encryption before Windows stops BitLocker (if enabled). Check compatibility between SSD and Windows and TPM and set which device should encrypt.
BitLocker Recovery
Following BIOS update or a change of a major component of the PC (like motherboard) BitLocker recovery key might become necessary.
As previously noted, you should have stored the key in a USB, Microsoft account or a print out (anywhere other than the hard drive that is protected).
- You can unlock BitLocker encrypted drive with the 48-character key
- Data recovery agents can unlock it using their credentials
- If you enabled proper BitLocker group policy setting the admin can unlock the drive
Also Read: How to Recover Data from Formatted BitLocker Encrypted Hard Drive?
Data Recovery From Encrypted Drive
What happens if a BitLocker-enabled drive fails and there is no access to hundreds of files with mission-critical data?
Common sense says that once the drive has failed, it is of no use trying to turn off BitLocker and Decrypt Drive. The drive is not working, how can it decrypt?
After all, encryption and decryption require the drive to be in full working condition and the file tables to be intact.
Microsoft’s own Windows File Recovery software leaves much to be desired. Not only does it not work perfectly but it is a CLI or command line utility that tends to confuse those who are not techies.
Using capable software such as Stellar Data Recovery Professional Software can solve your problem in as little as a couple of hours.
Features of Stellar Data Recovery Software:
- It can be installed on all PC Windows 7 onwards
- Can recover every type of file - images, documents, media with extensions, docx. pdf, mp3, flac, avi, mp4, wma, jpg, bmp, and many more.
- It can operate with all types of Windows partitions, FAT, exFAT, and NTFS
- Offers support for all types of HDD and SSD with PATA, SATA, and SCSI interfaces
- Perfectly decrypts and recovers data from BitLocker encrypted drives if the password is provided.
Also Read: How to Recover Files from Formatted Hard Drive For Free?
Stellar Data Recovery Software is the best data recovery software globally. It has a 5-star rating on Trustpilot and has earned the tag of #1 data recovery software in a survey by TechCrunch.
Our services are trusted by the best global business enterprises, from Google to Coca-Cola.
If you want to decrypt a BitLocker encrypted drive, download our software and recover 1 GB for free. If you are satisfied, buy the licence.
Go ahead and download it now.
About The Author

Content writer and digital marketing expert with 10 years of experience.



 Free Download
Free Download