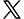What is JBOD?
JBOD stands for "Just a Bunch of Disks" or "Just a Bunch of Drives." It refers to a storage configuration where multiple hard drives are combined to create a single, larger logical volume without any redundancy
or special performance enhancements. Unlike RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks), JBOD does not provide data mirroring,
striping, or parity.
In a JBOD setup, each drive is treated as an individual unit, and the data is stored across the drives in a linear fashion. This means that if you have four 1TB drives in a JBOD configuration, you will have a total
of 4TB of usable storage space.

How Does JBOD Work?
In a JBOD configuration, drives are usually managed by a controller that aggregates them into a single logical volume. However, unlike RAID, JBOD does not employ any techniques to improve performance or provide fault tolerance. The primary advantage of JBOD is its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, as it does not require additional hardware or complex setup procedures.
Advantages of JBOD
- Flexibility and Simplicity: JBOD is a simple storage method. It enables the integration of disks with various capacities and speeds without requiring an intricate setup or specialized hardware controllers that RAID configurations frequently need.
- Storage Utilization: Multiple Solid-State Drives (SSDs) or hard drives are arranged in one enclosure under a JBOD storage architecture, unlike redundant arrays of independent disks (RAID) systems, which need more complicated data writing procedures.
- Cost-effective: Because JBOD uses current disks instead of requiring new hardware or identical drives, it can be less expensive than RAID.
Disadvantages of JBOD
- No Redundancy: Unlike RAID, JBOD does not provide any form of redundancy. If one drive fails, the data on that drive is lost.
- Performance: JBOD does not offer performance improvements like RAID 0 (striping) or RAID 1 (mirroring). The performance is typically the sum of the individual drives' performance.
- Data Management: Managing data across multiple drives can become cumbersome, especially as the number of drives increases.
Use Cases
The JBOD offers the highest application efficiency and accessibility due to its direct host attachment and expandable and adaptable capabilities. For many businesses and industries, JBOD systems represent a wise infrastructure investment.
JBOD arrays should be set up according to the particular requirements of the applications and production objectives of your company.
Some instances of this data storage solution in use are as follows:
- Cloud Storage and Data Centers: For application software hosting databases and transactional storage, where RAID-like data protection might not be necessary, JBOD systems are an excellent choice. JBODs can supply the necessary storage without charging extra for capabilities that might not be required for a given application.
- Entertainment and Media Sector: Media and entertainment companies need extensive storage to handle the editing of large amounts of video and other rich media assets. A JBOD (Just a Bunch Of Disks) can provide a scalable mass storage solution, serving as an intermediate layer for data in play. This helps these businesses maintain low costs while ensuring secure and effective temporary post-production workflow storage. The choice between HDD or SSD drives allows for optimized application performance.
- Security and Surveillance Systems: Video surveillance systems and archives require reactive mass storage to manage incoming video. JBOD devices are particularly useful for large-scale video management software, as they can receive and temporarily store incoming content efficiently.
Future Trends in JBOD Technology
JBOD systems are expected to undergo significant changes in the near future due to several key factors. The exponential rise in data storage requirements will be the primary driver of these changes. We anticipate the use of
higher-capacity drives in JBOD systems and support for newly developed storage technologies like SSDs.
Additionally, the growth of edge computing and IoT devices will likely lead to more decentralized and distributed JBOD solutions. This evolution will enable efficient and effective edge data processing.
Moreover, advanced data management features will become crucial. We expect JBOD systems to integrate encryption, deduplication, and tiering, enhancing their security and versatility.
Conclusion
JBOD is a straightforward and cost-effective storage solution that can be suitable for specific use cases where redundancy and enhanced performance are not critical. Its simplicity and flexibility make it an attractive option for media storage,
backups, and archiving. However, it’s essential to be aware of its limitations, particularly the lack of redundancy, which can pose a risk for data loss.
When choosing a storage solution, it's crucial to assess your specific needs
and consider factors such as cost, performance, redundancy, and scalability. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of JBOD, you can make an informed decision that best suits your storage requirements.
If you want to recover data from a RAID server, read this blog: How to Recover Data from RAID Server or RAID Server Recovery – What to Do If Your RAID Server Crashes.
If you want to learn about the benefits and drawbacks of RAID levels, read this blog: Advantages and Disadvantages of RAID Levels.
To choose the best between RAID 10 and RAID 5, check out this blog: Choosing the Best RAID Configuration for Enterprise: RAID 10 vs. RAID 5.
FAQs
When comparing the performance of JBOD vs. RAID, JBOD provides simple storage without any performance boosts but with independent disk capabilities. Performance is prioritized in RAID 0 setups, redundancy is the focus of RAID 1 designs, and a balanced approach is provided by RAID 5, 6, and 10.
If your data is stored on standalone hard drives, it is called JBOD. Your data will likely be lost if one of your JBOD disks fails. There is a place for both JBOD and RAID if you can effectively include them in your backup and data storage plans, making data recovery from JBOD easier.
JBOD is a multilevel disk setup, which stands for “just a bunch of disks.” It describes an array or group of disks merged into a single logical volume within a computer system.
JBOD lacks RAID parity, unlike RAID1, RAID5, and RAID6, which include RAID parity and can thus be increased. Data must be copied or backed up to another storage device or location before adding a new drive to a JBOD, and then the JBOD must be deleted.
You can find professional data recovery services near you by conducting an online search using keywords like "professional data recovery services near me" or "data recovery services in [your location]." Additionally, you can ask for recommendations from friends, colleagues, and IT professionals.
About The Author

Online Marketing Expert & Content Writer